Brand/nama lain
Fulcin, Gricin, Fungistop, Mycostop, Rexavin, Grivin Forte, Omefulvin
Cara Kerja
Griseofulvin termasuk dalam golongan obat antifungi (anti jamur) yang mampu mengobati infeksi yang disebabkan oleh jamur di kulit kepala, selangkangan atau lipat paha, dan kuku. Griseofulvin mengatasi infeksi jamur dengan cara menghambat pertumbuhan, perkembangbiakan, dan penyebaran jamur menjadi lebih luas ke sel-sel kulit yang sehat. Obat ini mampu mengendap di sel keratin yang ada di permukaan kulit, sehingga jamur tidak dapat menyerang ke lapisan kulit.
Indikasi
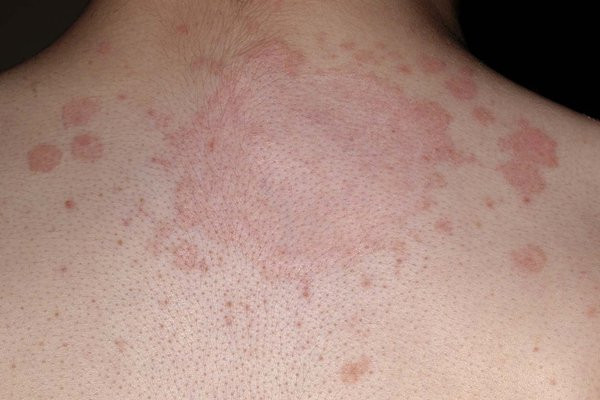
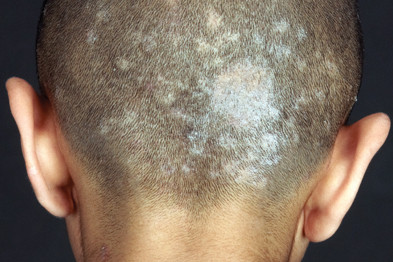
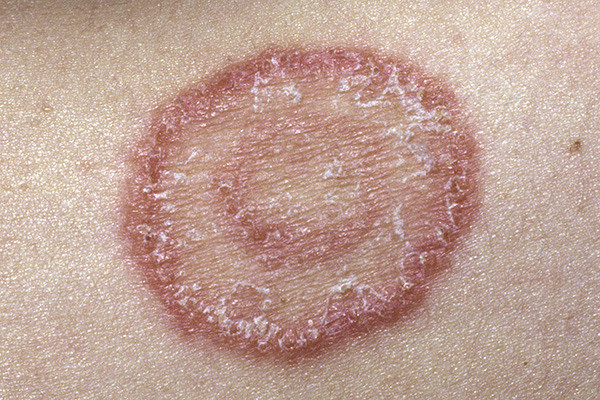
Griseofulvin adalah obat yang digunakan untuk mengatasi infeksi jamur di area kulit kepala, daerah lipatan tubuh, dan kuku. Obat ini efektif mengatasi keluhan gatal, kemerahan, dan kulit bersisik serta mengelupas akibat infeksi jamur. Griseofulvin umumnya digunakan untuk mengatasi infeksi jamur kulit setelah pengobatan dengan salep atau krim oles tidak efektif dalam menyembuhkan infeksi.
Griseofulvin dapat menghambat pertumbuhan berbagai spesies jamur seperti Microsporum, Epidermophyton, dan Trichophyton. Jamur tersebut umumnya menyebabkan infeksi kulit berupa tinea barbae, tinea capitis, tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea pedis, dan tinea unguium, yaitu infeksi jamur yang baisanya menimbulkan ruam melingkar kemerahan. Akan tetapi, Griseofulvin tidak memiliki efek anti jamur pada jamur jenis lain seperti Malassezia, Candida, atau Chromomycosis.
Kontraindikasi
Meskipun memiliki indikasi berupa infeksi jamur pada kulit, rambut, atau kuku, pasien tidak bisa menggunakan obat griseofulvin apabila memiliki beberapa kondisi yang bisa menjadi kontraindikasi terhadap kandungan griseofulvin, antara lain:
- Hipersensitivitas (alergi) terhadap griseofulvin maupun komponen formulasinya
- ibu hamil atau berencana hamil dalam satu bulan ke depan
- Ibu menyusui
- penderita penyakit porfiria
- gangguan pada hati
- lupus erythematosus sistemik
- anak berusia di bawah 2 tahun
Efek Samping
Penggunaan obat griseofulvin yang tidak sesuai dengan petunjuk atau dosis yang berlebih bisa menimbulkan beberapa efek samping tertentu. Efek samping yang mungkin terjadi selama pengunaan Griseofulvin, antara lain:
- Ruam kulit
- Urtikaria (reaksi pada kulit yang ditandai dengan munculnya bentol berwarna kemerahan disertai rasa gatal).
- Gangguan saluran pencernaan
- Mulut kering
- Perubahan rasa
- Sakit kepala
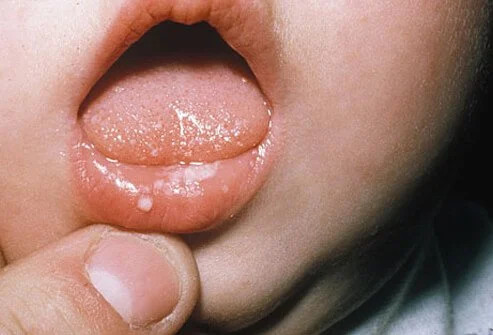
- Kandidiasis oral
- Fotosensitisasi atau sensitif terhadap cahaya
- Pusing
- Kebingungan
- Depresi, gangguan koordinasi, susah tidur, kelelahan
Efek samping griseofulvin yang cukup sering ditemukan adalah sakit kepala, reaksi saluran pencernaan berupa rasa tidak nyaman di perut, dan ruam erupsi pada kulit. Efek samping ringan yang paling sering terjadi adalah sakit kepala, dengan angka kejadian sekitar 15% dan efek samping tersebut dapat hilang dengan sendirinya.
Sediaan
Sediaan griseofulvin yang ada di Indonesia yaitu berupa tablet dengan dosis 125 dan 500 mg.
Dosis
Dosis griseofulvin ditentukan berdasarkan kondisi infeksi jamur yang dialami pasien. Secara umum dosis griseofulvin adalah sebagai berikut:
- Dewasa: 500 mg per hari 1 x sehari, atau 250 mg 2 x sehari. Untuk infeksi yang lebih berat: 1000 mg x 1 kali sehari, atau 500 mg 2 x sehari.
- Anak usia ≥2 tahun: 10 mg/kgBB per hari, untuk 1 kali konsumsi atau dibagi ke dalam beberapa kali pemberian.
Lama pengobatan untuk tinea di kulit berkisar antara 2–8 minggu, tergantung pada jenis infeksi jamur yang dialami pasien. Sementara untuk infeksi jamur di kuku (tinea unguium), lama pengobatan minimal adalah 4 bulan pada kuku tangan dan 6 bulan pada kuku kaki.
Keamanan
Kehamilan:
Griseofulvin termasuk dalam FDA Kategori X yang mengindikasikan bahwa penggunaan obat griseofulvin pada kehamilan tidak disarankan, karena dilaporkan dapat meningkatkan risiko malformasi atau kecacatan pada janin.
Menyusui:
Penggunaan pada ibu menyusui juga sebaiknya dihindari, karena keamanannya belum didukung data ilmiah yang cukup.
Interaksi Obat
Berikut ini beberapa interaksi antar obat yang dapat terjadi apabila griseofulvin digunakan bersamaan dengan obat lain:
- Penurunan efektivitas obat antikoagulan, seperti aspirin, warfarin, atau heparin
- Penurunan efektivitas ciclosporin
- Penurunan efektivitas pil KB
- Penurunan penyerapan griseofulvin jika digunakan bersama fenilbutazon, barbiturat, obat penenang, atau obat tidur
- Penurunan efektivitas obat kemoterapi, seperti vinorelbine atau nilotinib
- Peningkatan risiko terjadinya sunburn jika digunakan bersama aminolevulinic acid
Mau tahu informasi seputar obat-obatan lainnya? Cek di sini, ya!
- dr. Alvidiani Agustina Damanik
MIMS Indonesia. Griseofulvin. Retrieved 17 August 2024, from: https://www.mims.com/indonesia/drug/info/griseofulvin?mtype=generic
Mayo Clinic Drugs and Supplements. Griseofulvin (Oral Route). Retrieved 18 August 2024, from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/griseofulvin-oral-route/proper-use/drg-20064116
U.S. National Library of Medicine National Center for Biotechnology Information. Griseofulvin. Retrieved 18 August 2024, from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537323/
U.S. National Library of Medicine. National Institute of Health MedlinePlus. Griseofulvin. Retrieved 19 August 2024, from: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682295.html
Medscape Drugs & Diseases. Griseofulvin. Retrieved 19 Augsut 2024, from https://reference.medscape.com/drug/grifulvin-v-gris-peg-griseofulvin-342590